字典简介
dict(dictionary字典),是一种以key-value形式存储的数据结构;通过hash函数对key求hash值获取value的位置,因此也叫hash表,是一种用来解决查找问题的数据结构,时间复杂度接近O(1)。对于Redis,它本身也叫REmote DIctionary Server,其实就是一个大字典,它的key通常来说是一个String类型,value的值可以是String,Set,Zset,List,Hash等等类型。
字典这种数据结构我们用的很多,比如python中的dict,java中的map,都是有原生接口的方法;对于C中没有原生的dict接口,需要我们自行定义,下面来看看redis中的字典是如何定义和实现的。
数据结构定义
这里阅读的是redis 5.0版本。
源码位置:
- dict.h:dictEntry,dictht,dict等数据结构的定义;
- dict.c:创建,插入,删除,查找等功能定义;
与dict相关的主要数据结构有三个:
- dictEntry:表示一个key-value节点
- dictht:表示一个hash table
- dict:redis中的字典结构,hash table的入口,包含两个dictht
dictEntry的代码:
typedef struct dictEntry {
void *key; //key void*表示任意类型指针
union { //联合体中对于数字类型提供了专门的类型优化
void *val;
uint64_t u64;
int64_t s64;
} v;
struct dictEntry *next; //next指针
} dictEntry;
dictht的代码:
typedef struct dictht {
dictEntry **table; //数组指针,每个元素都是一个指向dictEntry的指针
unsigned long size; //表示这个dictht已经分配空间的大小,大小总是2^n
unsigned long sizemask; //sizemask = size - 1; 是用来求hash值的掩码,为2^n-1
unsigned long used; //目前已有的元素数量
} dictht;
dict的代码:
typedef struct dict {
dictType *type; //type中定义了对于Hash表的操作函数,比如Hash函数,key比较函数等
void *privdata; //privdata是可以传递给dict的私有数据
dictht ht[2]; //每一个dict都包含两个dictht,一个用于rehash
int rehashidx; //表示此时是否在进行rehash操作
int iterators; //迭代器
} dict;
手画了一下大致的数据结构图:
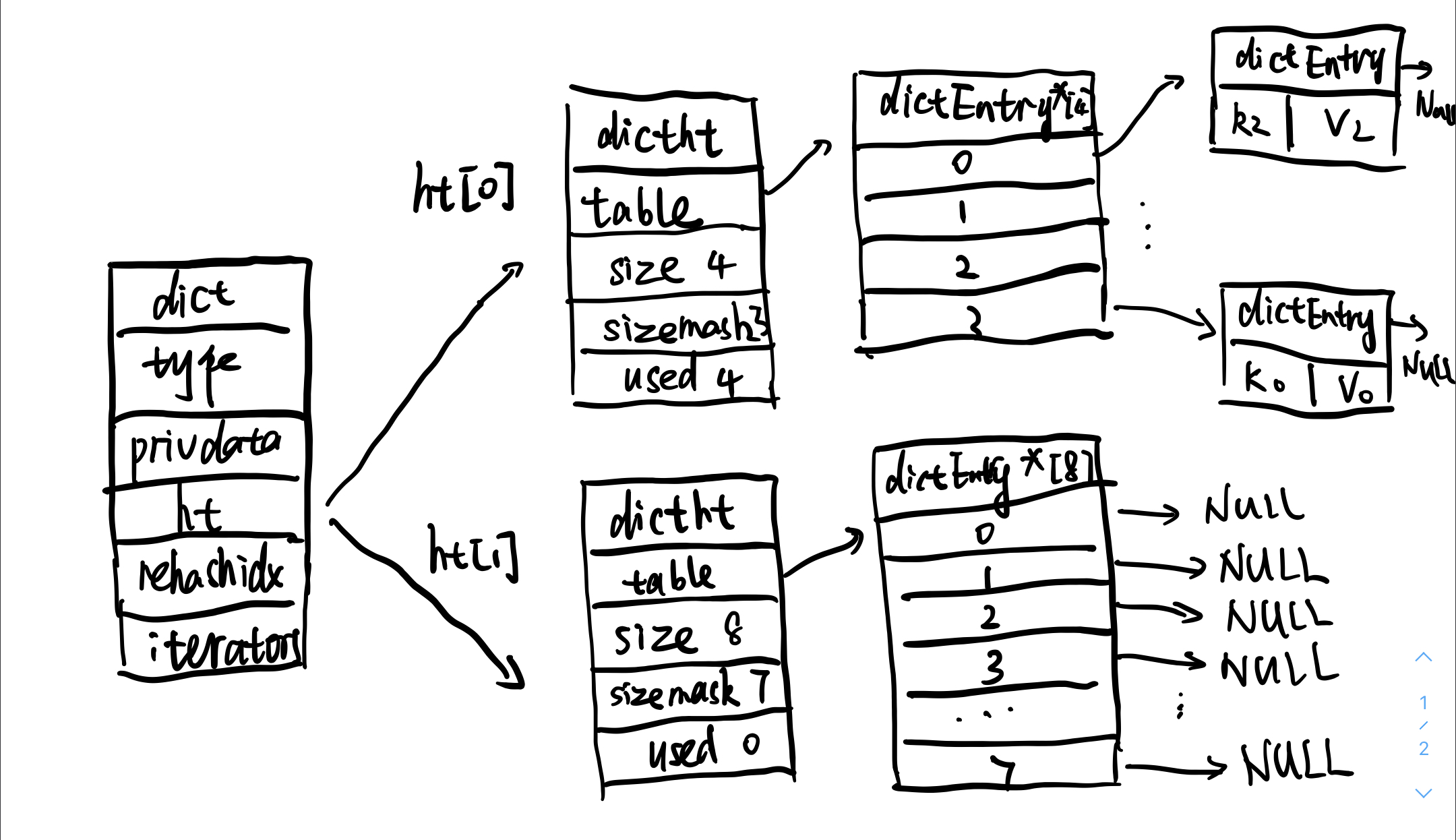
通过图中的方式,把三个数据结构结合起来形成redis的字典。
增删改查相关
一、创建
先来看看代码,
/* Create a new hash table */
dict *dictCreate(dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
dict *d = zmalloc(sizeof(*d)); //申请空间
_dictInit(d,type,privDataPtr); //初始化d
return d;
}
初始化部分,主要是把type和privdata等值设为默认值
/* Initialize the hash table */
int _dictInit(dict *d, dictType *type,
void *privDataPtr)
{
_dictReset(&d->ht[0]);
_dictReset(&d->ht[1]);
d->type = type;
d->privdata = privDataPtr;
d->rehashidx = -1;
d->iterators = 0;
return DICT_OK;
}
二、插入
这部分主要涉及到三个函数,dictAdd、dictAddRaw和_dictKeyIndex
/* Add an element to the target hash table */
int dictAdd(dict *d, void *key, void *val)
{
dictEntry *entry = dictAddRaw(d,key,NULL);
if (!entry) return DICT_ERR;
dictSetVal(d, entry, val);
return DICT_OK;
}
在dictAddRaw函数中,创建了dictEntry,即key-value节点,
dictEntry *dictAddRaw(dict *d, void *key, dictEntry **existing)
{
long index;
dictEntry *entry;
dictht *ht;
if (dictIsRehashing(d)) _dictRehashStep(d); //检查是否正在rehash
/* Get the index of the new element, or -1 if
* the element already exists. */
if ((index = _dictKeyIndex(d, key, dictHashKey(d,key), existing)) == -1)
return NULL;
/* Allocate the memory and store the new entry.
* Insert the element in top, with the assumption that in a database
* system it is more likely that recently added entries are accessed
* more frequently. */
ht = dictIsRehashing(d) ? &d->ht[1] : &d->ht[0];
entry = zmalloc(sizeof(*entry));
entry->next = ht->table[index];
ht->table[index] = entry;
ht->used++;
/* Set the hash entry fields. */
dictSetKey(d, entry, key);
return entry;
}